CBN Oil Extraction -- A Complete Guide to Extracting Cannabinol
CBN, also known as cannabinol, is one of the many cannabinoid derivatives produced by the wonderfully complex cannabis and hemp plant. CBN oil, along with the more well-known CBD oil (cannabidiol) and lesser known CBG oil (cannabigerol), is gaining consumer attention because of its potential benefits without the typical “high” associated with THC (although it does appear to have very mild psychoactive effects known for promoting restful sleep).
As consumers become more informed about medical and wellness-related use of hemp and cannabis they also are becoming more sophisticated in their search for “new” cannabinoid derivatives. Therefore, the smart money in the industry is producing trending cannabinoids such as CBN. In such a fast-evolving industry—and in such volatile times—it makes sense to diversify your efforts and not put all your eggs into the one cannabinoid “basket”.
But what is CBN? What is CBN oil good for? How does CBN affect the human body? And most importantly, will extracting it help your extraction business to grow?
What is CBN Oil AKA Cannabinol?
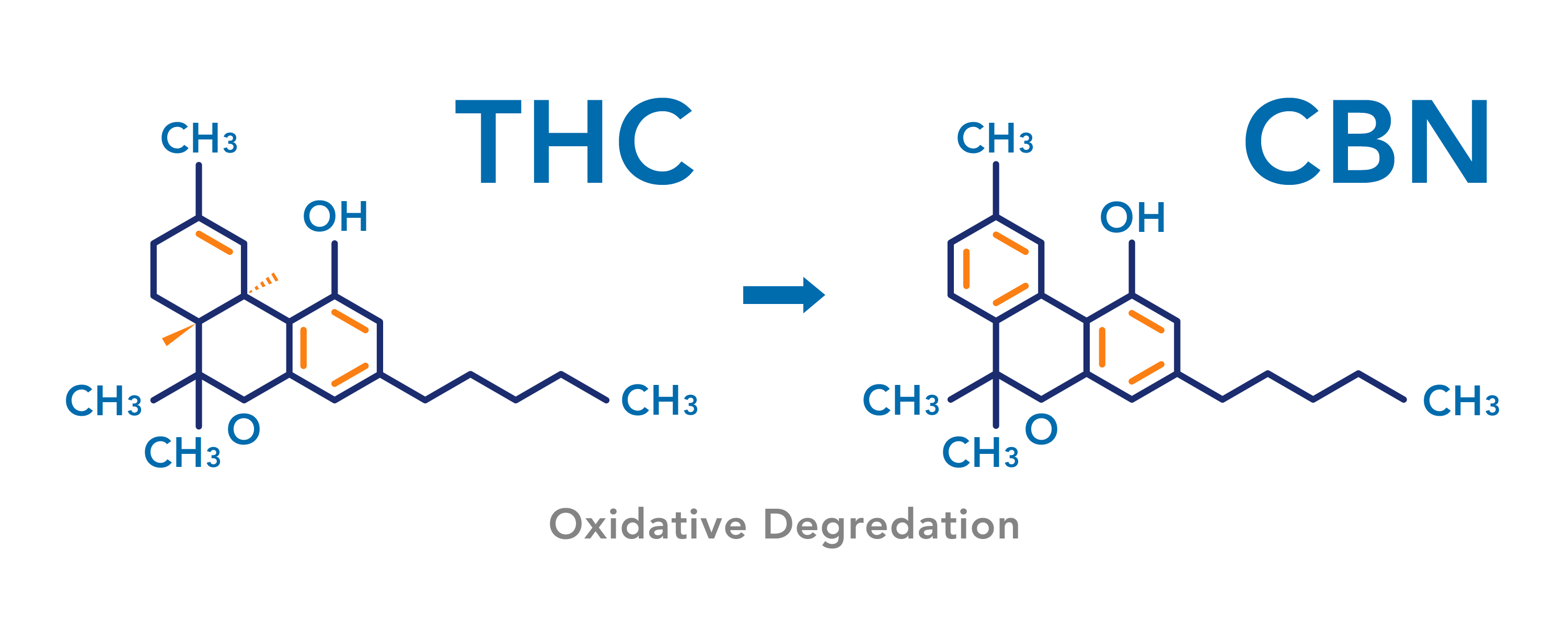
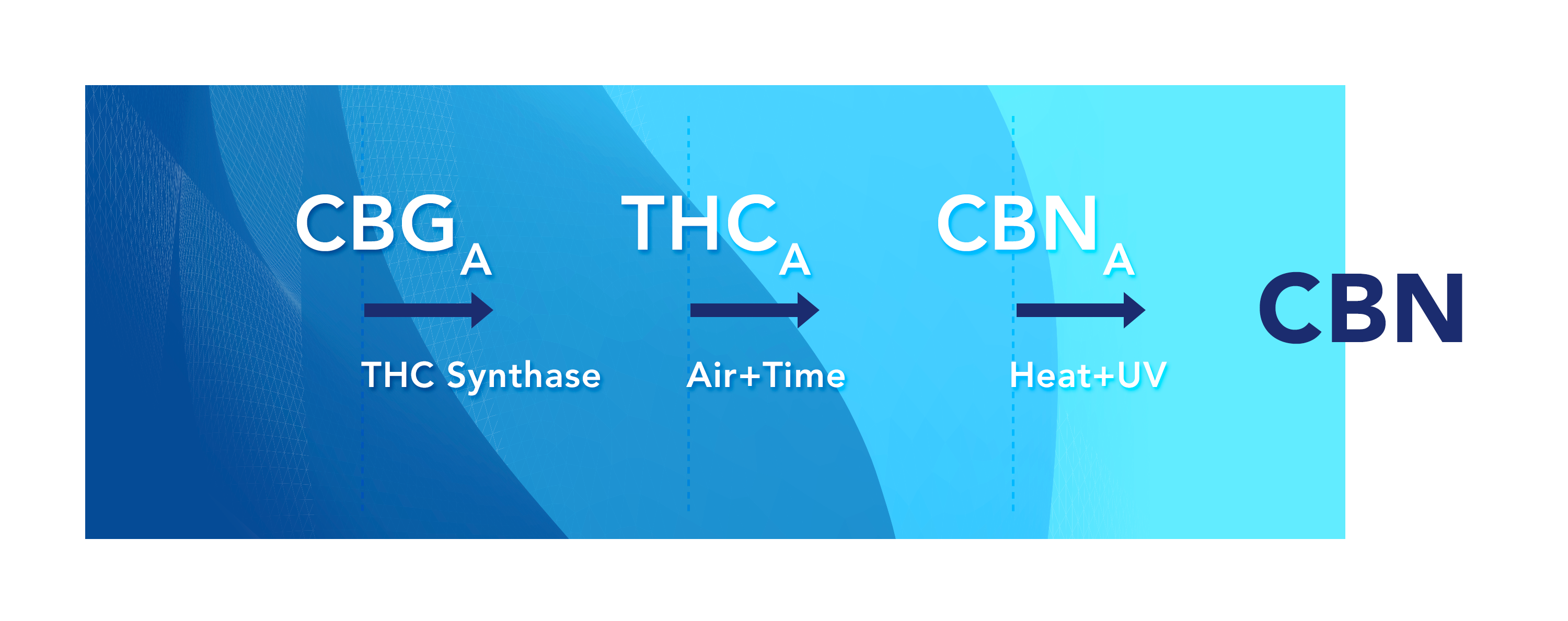
Cannabinol (CBN) is a cannabinoid typically found in aged or oxidized cannabis or hemp because it is the product of degraded tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa). Unlike most other cannabinoids CBN isn’t a cannabinoid that is formed from the “mother cannabinoid” CBG, but rather is a byproduct of the aging process.
When cannabis is exposed to air or ultraviolet light (e.g. UV rays in sunlight) for too long, the THCa converts to cannabinolic acid (CBNa). The CBN molecule is then produced by decarboxylating CBNa. Low-quality baled cannabis and traditionally produced hashish are high in CBN but in contemporary use it is most often extracted as an isolate to be added to various end-products such as gel caps, sublingual drops, and tinctures.
CBN vs. CBD: What is the difference?
While both cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) come from the same hemp or cannabis plant, it is in fact the processing of this plant that decides on the levels of CBN produced. The level of CBN in a cannabis bud depends on its age and the amount of light and heat it has been exposed to.
From a wellness perspective CBD and CBN are quite similar however and are often sold together because they have complementary purported effects on the human body. Both are only mildly psychoactive in that they may relieve anxiety and promote relaxation and restful sleep but will not give you the visceral “high” of THC.
But they may also be used along with recreational cannabis THC products to affect the kind of high you desire, for example, to promote couch lock, sleep, or general relaxation. CBN and CBD may also be helpful for those who have taken too much THC and want to reduce any feelings of paranoia or anxiety that may result.
Is CBN oil legal to extract?
The legality of CBN oil falls into a grey area. On the one hand, CBN is not listed as a scheduled controlled substance in the U.S. However, CBN could possibly legally be considered an analog of THC or CBD, both of which are Schedule I substances if derived from cannabis rather than from hemp that has less than 0.3% THC. And therefore, sales or possession could potentially be prosecuted under the Federal Analogue Act.
In December 2016, the Drug Enforcement Administration added marijuana extracts, which are defined as any “extract containing one or more cannabinoids that has been derived from any plant of the genus Cannabis, other than the separated resin”, to Schedule I. This action has led to additional uncertainty about the legal status of CBN.
Thanks to the passage of the 2018 Farm Bill that legalized hemp and all the plant’s derivatives, CBN oil is legal at the federal level in the United States but only it’s derived from hemp—not cannabis. Hemp is legally defined as a cannabis plant that contains less than 0.3% THC. The consensus seems to be that if you extract your CBN from hemp you’ll remain on the right side of federal law. But state-by-state laws of course, may differ.
*NOTE: at the time of writing, all cannabis and cannabis-derived compounds remain illegal at the federal level.
What does CBN oil do for the body?
It’s very important to note that any discussion around health benefits of CBN comes with a disclaimer in that all the data comes from very early studies and experiments. For decades most cannabis or hemp cannabinoid derivatives were strictly “off limits” for studying in most countries due to their illegal classification, especially in the US. So, we have little to go on but there exist some very positive early studies and anecdotal evidence on how CBN has a beneficial affect the human body in several ways.
To outline the effects of CBN on the body we need to look at how the body interacts with this relatively newly discovered cannabinoid derivative. The human nervous system has two types of endocannabinoid receptors to make up the Endocannabinoid System (ECS):
- CB1: found in the central nervous system, and,
- CB2: found in your peripheral nervous system, especially in immune cells
Endocannabinoids bind to these two receptors in order to signal that the ECS needs to act in some way. The action will differ depending on the endocannabinoid that is interacting with the ECS. For example, endocannabinoids may target CB1 receptors to relieve spinal pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor to reduce inflammation in your immune system.
Cannabinol has a greater binding affinity for the CB2 receptor than the CB1 receptor. CBN acts as an agonist at the CB1 receptors, albeit with much less strength than THC.
CBN is also an agonist at TRPV2 receptor, potentially contributing to exert pain-relieving responses from our endocannabinoid system so ideal for pain relief.
If you want more information on how the ECS system works here’s a link to a detailed peer-reviewed study on CBN and other cannabinoids from 2017.
Is CBN good for sleep and anxiety?
The short answer is that CBN may promote restful sleep and anxiety relief. But like most cannabinoids, CBN works better not as an isolate but when it’s used along with THC, other minor cannabinoids, and terpenes in what’s known as “full spectrum” extracts.
The longer answer is that there are few studies out on the Internet that show promise but nothing conclusive. One is from 1995 and showed that CBN in mice can prolong time asleep. Some earlier research from 1975 indicated that the sedative effects of CBN are enhanced when used along with THC. Anecdotal evidence supports this. Many so-called “recreational” users of THC-rich cannabis are in fact using it therapeutically. They use cannabis derivatives in the evenings to help them wind down and sleep, often choosing Indica strains high in CBN and sleep-promoting terpenes.
Another study shared by Steep Hill Labs in 2017, found that a 2.5-to-5 milligram dose of CBN was as effective as a 5-to-10 milligram dose of the pharmaceutical sedative diazepam (otherwise known as Valium). But this study has not been repeated.
So, is CBN good for sleep? We really don’t know yet because not enough study has been done on the topic nor on how cannabinoids—in general—interact with the human body.
Is CBN good for inflammation and pain relief?
Scientific research indicates that CBN has analgesic or pain-relieving capabilities. CBN appears to influence the activity of neurons that are sensitive to capsaicin. These neurons are critical players in the body’s pain perception system. Here’s a link to a study from 2002 that explores the effect of CBN and THC on CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Using a cannabinoid derivative such as CBN (along with ratios of THC and perhaps CBD) for pain relief is ideal for those people who may have reached an efficacy threshold with pharmaceutical pain relievers and/or do not wish to become dependent to strong opioids such as Oxycodone after accident or illness.
In fact, many experts in the fields of addiction and rehabilitation are using cannabinoid derivatives to help people to be free from opioid addiction—most especially CBD and THC ratios—which are gaining reputation as the new “exit drug” for addiction.
What are the most popular ways to take CBN?
The most popular CBN products include oils, tinctures, edibles, topicals (creams and lotions), and gel capsules. As an extractor, however, everything depends on whether you want to sell CBN as a “white label” isolate or make your own full-spectrum end-products to sell at retail.
Regardless of your choice, to ensure the cannabinoid content of a CBN or full spectrum product, it is critical to ensure the cannabis or hemp derivative has been independently tested by a third-party testing lab before releasing it onto the market.
You’ll also need to make sure that there is less than 0.3% THC content (or none, just to play it safe) to ensure that you don’t attract attention of law officers in states where THC is illegal.
Can I Convert THC into CBN?
Yes, you can convert THC into CBN which may offer a way for extractors to diversify their cannabinoid derivative end-product portfolio to adapt to the changing demands of the marketplace. For example, you may have a backlog of THC and you may make more revenue from CBN so it may be profitable to pivot and convert your THC into CBN.
Lance Griffin from Extraction Magazine writes:
“The most common and obvious strategy beyond natural aging is to apply heat. According to Wang et al, “Δ-9-THC itself readily oxidizes to cannabinol (CBN) with oxygen and light during the decarboxylation process.” A different study published in 2005 found that this oxidation occurred above 150° C (302° F) given a 15-minute decarboxylation period. The typical decarb process employs lower temperatures and longer times to avoid this conversion and preserve Δ-9-THC; amping up the temperature may thus prove useful for CBN seekers. However, using a vacuum oven mitigates this conversion.” Read the rest of Lance Griffin’s article here.
The other strategy for converting THC into CBN is the use of UV light as an alternative to heat. As mentioned previously, light degrades cannabis and hemp, facilitating a natural conversion of THC into CBN.
However—and here’s the catch—to extract CBN at a large scale in a lab setting, neither UV light nor heat is used to convert THC to CBN for the purposes of isolation. Typically, it is a much more complicated and well-guarded proprietary SOP involving refluxing the THC, dissolved in specific solvents, and usually in the presence of precious metal catalysts.
How do I Extract CBN oil from cannabis or hemp?
Before even starting the process of extracting CBN you need to start with biomass that is high in the precursor to CBN, which is CBNa. To gain a high concentration of CBNa you need to age your cannabis or hemp biomass and expose it to UV light. How much light and how much aging will your material need? That depends on the CBNa content potential in your strain of choice so, obviously, it will vary from strain to strain. However, there are a few strains that are known for their high concentration of CBN:
- Blackberry
- Bubble Gum
- Durban Poison
- Lemon Kush
- Purple Cadillac
- Super Green Crack
The actual extraction and refinement process of CBN is very similar to most other highly sought-after cannabinoids. CBN is extracted through a process that uses ethanol or CO2 as a solvent—or even both if you want to ensure that you’ve have extracted everything from your CBN rich biomass. For example, you can use CO2 to pull the fragile terpenes and then use ethanol to extract everything else for a full-spectrum, highly concentrated CBN oil.
The CBN Extraction Process
The CBN extraction process begins by soaking the biomass in your solvent of choice (typically either CO2 or ethanol) to separate out the terpenes and/or cannabinoids from the biomass. The resulting solution is then put into an evaporator using heat and a vacuum to remove the solvent. This results in a refined CBN crude extract. The crude concentrate is then further distilled to create a purified distillate.
The CBN extraction process typically flows something like this (for our purposes here, a Cold Temperature Ethanol Extraction process flow):
- Chilling: Pre-chill ethanol solvent using the DC-40 Direct Chiller to as low as -40c to reduce post-extraction steps.
- Extraction: Soak cannabis biomass in chilled ethanol solvent to extract cannabinolic acid (CBNa) compounds via CUP Series closed-loop mechanical centrifugation.
- Particulate Filtration: Remove any suspended particulates/adsorbents
- Solvent Evaporation: Remove ethanol from plant crude oil using the Falling Film Evaporator (FFE).
- Decarboxylation: Activate CBNa to produce CBN (and possibly CBD, THC, etc. depending on your biomass) by removing carboxyl group.
- Distillation: Separate CBN molecules from crude oil utilizing Rolled Film Distillation (RFE).
- HPLC: Test distillate to measure concentration of CBN molecules.
A key part of the CBN purification process is the use of chromatography, most specifically, with a High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) device. This apparatus helps the operator isolate and purify CBN extracts to ensure the best results. It is difficult to ensure a high-quality end-product without using HPLC. The chromatography apparatus can be very expensive, so if your lab does not already own this equipment, it bears keeping the potential cost in mind when setting up your CBN extraction operation.
CBN Extraction Equipment and Systems
What equipment and systems will you need to extract CBN? The following recommended equipment is based on the two most popular forms of CBN extraction: ethanol and CO1. We recommend the following:
- DC-40 – Direct Chilling: The DC-40 Direct Chiller eliminates the use of cumbersome ultra-low freezers. A vital step in cold extraction of CBN. Quickly chill alcohol pre-extraction within a compact footprint, saving lab space and post-processing time.
- The CUP Series alcohol extraction systems enable targeting of CBNa oil compounds from cannabis and hemp. The CUP series is an all-in-one unit that washes and dries the biomass in the same closed-loop system. Boasting a 97% alcohol removal from biomass, the CUP series streamlines production times and maximizes extraction yields.
- FFE Series Evaporator – Falling Film Evaporator: Recommended for cannabinoid separation and ethanol alcohol recovery from your extracted CBNa tincture. The system maintains a high evaporation rate, which significantly increases the throughput of crude oil production, eliminating the need for multiple large rotary evaporator systems.
- RFD-27 – Rolled Film Distillation: is the final step in the processing of high-quality CBN distillate. The RFD-27 is engineered to refine targeted compounds from cannabis and hemp extracts to deliver clear distillate at fast speeds. Durable stainless-steel construction enhances heat transfer capacity.
- High-Output CO2 Systems:
- The Force: The Force® systems efficiently extract CBN oil without thermal degradation at industry-leading processing rates. These systems provide high production with a wide range of processing options for supercritical and subcritical extractions.
- The Fleet (Hemp Processing System): The Fleet allows you to add up to three systems to one single outdoor chiller. The effect of daisy chaining systems means your capacity is increased, yet your energy efficiency is not increased as well because of the single chiller that operates all three systems.
- Recommended Ancillaries:
- Lenticular Filtration Skid: Ethanol filtering solution filters ethanol between extractions on the CUP-15/30 to allow the DC-40 to maintain solvent temperature so the same solution can be used for up to 3 bags of biomass.
- Ai Glass reactor 50-100+L, multiple (residual solvent removal + decarboxylation)
- Ai / Buchi; Rotary Evaporator:50L, multiple (final solvent evaporation)
- Hipersep Pilot: Medium scale affinity chromatograph for isolation of cannabinoids used for method design ahead of large-scale application.
Getting Started with CBN Extraction
Thinking of getting started with CBN extraction? Or, are you a practicing extractor thinking about adding CBN to your end-product portfolio? We can help! Please contact us at +1(800) 837-1333 or email sales@deltasepaprod.wpengine.com.